Now Reading: Building Resilience with Modern Commercial Restoration Techniques
-
01
Building Resilience with Modern Commercial Restoration Techniques
Building Resilience with Modern Commercial Restoration Techniques

Climate change, urban needs, and rising costs are transforming commercial property design, maintenance, and revitalization. Owners acknowledge that resilience extends beyond repairs, emphasizing innovation, environmental responsibility, and future-proofing—upgrading outdated structures for longevity and adaptability. Investing in resilience involves proactive measures, using advanced materials, smart tech, and sustainable designs to improve efficiency and protect architectural heritage for future challenges.
Innovative Materials in Commercial Restoration
The field of commercial building restorations has experienced breakthroughs in materials science, fundamentally changing how buildings are reinforced and protected. One of the most notable advancements is the adoption of Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP). FRP offers remarkable strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for significant structural improvements without adding massive weight or requiring invasive construction. Using FRP wraps, contractors can bolster aging beams and columns, extending the lifespan of buildings while controlling costs.
Other modern material solutions include self-healing concrete and high-performance sealants, which reduce the need for frequent repairs and prevent damage from moisture or temperature fluctuations. These advanced materials offer an attractive alternative to traditional methods, addressing structural integrity and long-term durability.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Resilience
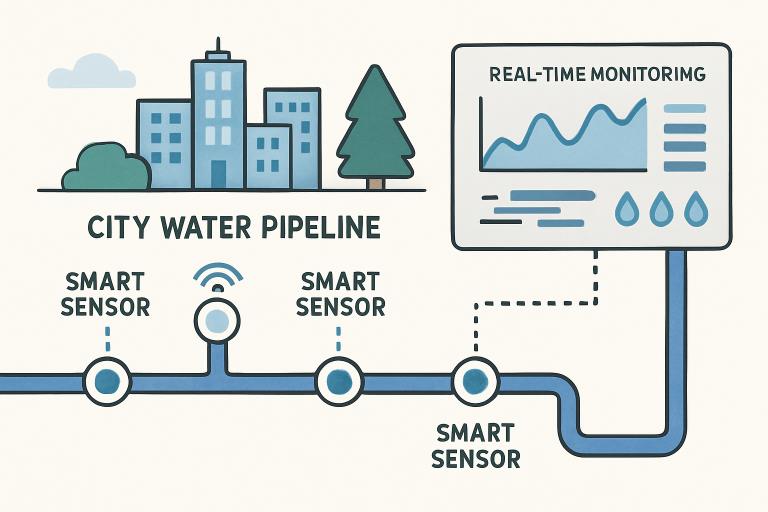
Technology plays a pivotal role in the modern restoration process. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is at the heart of this shift, enabling teams to create precise 3D models of existing structures. These digital models facilitate comprehensive damage assessments, transparent communication, and more accurate planning—minimizing errors and costly surprises during restoration.
Digital twins—creating real-time, virtual replicas of physical buildings—further advance resilience. These models allow owners to monitor conditions remotely, schedule predictive maintenance, and quickly pinpoint vulnerabilities before they escalate. The result is a smarter, more responsive approach to building management. Digital twins represent the forefront of proactive facility resilience and operational efficiency.
Sustainable Practices in Building Restoration
Restoration efforts today are inseparable from sustainability goals. Building retrofits focus on upgrading systems to reduce energy use and costs. Retrofitting with energy-efficient HVAC, lighting, and controls is common. Panelized cladding systems installed over facades create a sealed, insulated envelope that minimizes energy loss while preserving the structure. These strategies lower energy bills, support LEED certification, and boost property value. Using renewable energy like rooftop solar and recycled materials accelerates the move toward a low-impact, high-performance built environment.
Adaptive Reuse and Historic Preservation
Adaptive reuse revitalizes existing structures by transforming them for contemporary purposes, such as converting warehouses into offices, thereby preserving cultural and architectural heritage. This approach reduces environmental impact and restoration expenses while retaining valued historical character. Projects like converting Sioux Falls’ Sawtooth Building into collaborative workspaces demonstrate how design and material enhancements can respect the past while meeting present-day demands. Beyond its ecological advantages, adaptive reuse cultivates a sense of place and continuity, helping cities maintain distinct identities amidst development and modernization.
Case Study: Modernizing Historic Buildings
The Idaho State Capitol Building’s recent restoration reflects the advantages of combining new technology with a respect for history. Engineers and conservationists worked together to retrofit the structure with energy-efficient lighting, upgraded HVAC systems, and sustainable materials while preserving the building’s distinct architectural features. The project exemplifies how modern techniques can support resiliency and preservation, safeguarding the state’s heritage against environmental and operational risks.
Such efforts demonstrate that ambitious restoration can elevate historic structures to meet 21st-century standards without sacrificing authenticity. These projects create sustainable spaces that inspire civic pride, attract investment, and ensure longevity. Major modernizations like this serve as blueprints for balancing innovation, sustainability, and preservation in commercial building restorations.
Conclusion
The intersection of innovation, sustainability, and preservation redefines the future of commercial building restoration. By leveraging advanced materials, cutting-edge technologies, and eco-conscious designs, property owners and developers can create resilient buildings ready to meet the demands of tomorrow. Adopting modern commercial building restorations is essential—offering enhanced safety, efficiency, and historical value for future generations.